4 Steps to Healthy Weight Management
Most people desire to make changes to their health and usually begin with wanting to lose weight. They have a vision and a goal number they want to see on the scale so they set goals and action steps to reach this weight loss.
Often, however, many individuals may reach their goals but then find that the weight loss doesn’t last. Or, they may not know the exact steps that are required for them to reach their weight loss goals. Instead, they find themselves on a rollercoaster without consistency. What is the missing piece? Seeking guidance from professionals, like the Huntington Beach Christian Counseling, to help you develop a sustainable plan and stay motivated.
Having healthy weight management.
If you’re thinking about making changes to maintaining your weight, it can be a difficult road to find what is best for you, your body, and your lifestyle. The majority of our thoughts are centered around the foods we choose and how much we exercise. While this is true, there are missing components to successfully find balance and ease with being able to maintain healthy stability.
Having a healthy weight management goal instead of a weight loss goal may just be the perspective shift you have been looking for all along! When you focus on what healthy weight management looks like for you, you can be set free from needing to try different diets or setting a goal weight because you begin to understand what is right for your body naturally.
In this article, you are going to learn four steps to find and successfully implement lasting healthy weight management.
Step One: Understanding your digestive health
Your digestive health is the first place you need to look when it comes to your ability to manage a healthy weight. In the context of weight management, the amount of stress you are dealing with, the number of inflammatory foods you are consuming, and the overall health of your gut are paramount and also work in tandem.
 Your digestion begins before actually eating food as it relates to external factors like stress and anxiety that unknowingly greatly affect how your foods are digested. Additionally, if your diet consists of food high in sugar or processed, your gut lining and proper functions of your digestion will be impaired due to the constant state of inflammation.
Your digestion begins before actually eating food as it relates to external factors like stress and anxiety that unknowingly greatly affect how your foods are digested. Additionally, if your diet consists of food high in sugar or processed, your gut lining and proper functions of your digestion will be impaired due to the constant state of inflammation.
This is what can cause unhealthy cravings or addiction to sugary foods. When you learn to choose the right foods that are anti-inflammatory and eat for your digestion, you’ll immediately see improvements and see your body remarkably adapt to its natural healthy state.
Step Two: Define what is healthy management
As above-mentioned, focusing on setting a healthy weight management goal instead of a weight loss goal will help you in the long run. Every day we are bombarded with advertisements, promotions, and sales for healthy foods, products, supplements, and diets. Through social media channels, magazines with headlines on the front cover, or even if you ask Google what is healthy management, it’s very noisy!
What happens is that all of the images, phrases, diets, and advertisements that we see, subconsciously begin to build the wrong impression of what is right and true for your health. It becomes easier to focus on all of the things you “should” be doing instead of learning, knowing, and understanding what is right for you and your body. The key factor is to read between the lines and find what you need for your health.
How do you do this?
The answer is to set a goal for success. Before you begin a new health journey, ask yourself these four questions:
- What does my desired weight management look like?
- How will I know when I am successfully managing my health?
- What is my desired look, feel, and lifestyle?
- Why am I choosing to focus on maintaining my weight?
When you take the time to ask yourself these four questions, you are setting yourself up for success before you even begin. What happens is that most individuals want to choose better foods, make changes to their eating and exercise habits, and immediately jump into the new diet that everyone is speaking about, such as the one that promised instant results that you read about on the magazine cover while waiting in line at the grocery.
 So because this is all the craze, many people rush into then buying those suggested ingredients, supplements, or diet plans without truly preparing for the course that aligns with long-term sustainability.
So because this is all the craze, many people rush into then buying those suggested ingredients, supplements, or diet plans without truly preparing for the course that aligns with long-term sustainability.
Maintaining a healthy weight goes beyond the food choices and amounts of exercise because it has everything to do with your reasons, definitions, and lifestyle. If you never measure what success in this area means to you, how will you know when you have reached it?
If you do a personal inventory, you may already be maintaining your weight from a goal you set years ago, but without knowing what it looked like back then, it’s easy to want to keep doing new things because without realizing that you already met your initial goal.
When you consider what asking yourself these four questions means to you, you will start to see the connection between the how, what, why, and your will. These four questions are pivotal in helping you set your vision and determine what steps are needed to help you reach your goals. Coupled with a better understanding of your digestive health, you’ll be empowered to choose the right foods for long-term health rather than short-term satisfaction.
Step Three: Find an activity you love to do
One of the largest areas where people “fall off the wagon” is not loving what they were committed to doing, especially in the area of exercise. Most people end up feeling less motivated because it resembles a chore that interrupts their day and must be done. When you find an activity you love to do, your inspiration is automatic and you end up excited about it, becoming naturally committed.
 When it comes to exercise, try an activity that is something new and different. Notice the change in words from exercise to activity. Placing your focus on a daily activity also changes your perspective from it feeling like a chore. Make small commitments then increase your frequency over time. When trying a new activity and you realize you don’t like that one you picked, try something new. Exercise does not have to be hours on a treadmill or doing squats.
When it comes to exercise, try an activity that is something new and different. Notice the change in words from exercise to activity. Placing your focus on a daily activity also changes your perspective from it feeling like a chore. Make small commitments then increase your frequency over time. When trying a new activity and you realize you don’t like that one you picked, try something new. Exercise does not have to be hours on a treadmill or doing squats.
Finding new trails in nature with gorgeous views. You can even try switching up the times you decide to commit to your activity and couple it with a benefit, much like going on a walk to go watch the sun rise or set. Consider trying a new sport and joining a league like rowing, softball, or volleyball. Sometimes when you reflect on a sport you used to play when you were young, you may find you are inspired to pick it back up as an adult. What is on your list to try?
Step Four: Fight those negative thoughts
Another contributing factor to why it is difficult to maintain a healthy weight is because we let our thoughts and words defeat us. Sometimes when it comes to not seeing progress as soon as one thought would happen allows an open door for negativity, frustration, and setbacks to enter in.
When you act upon the four questions you attached to your goal (hint: see step two), you end up staying committed to the lifestyle goal you are seeking instead of the feelings when you let negativity lead.
With that said, when you surrender your health to God’s power, you can maintain anything when you rely upon His strength. Another encouragement is to study Scriptures that reflect your goals and partner with the Holy Spirit to pour out His ability for you to stay committed to your health management goals.
If you are looking to take these four steps in a practical way, consider coaching. When you work with a coach, you get to discover and design your goals through a series of questions to help you get clear on your vision and steps. Not only do you get to make a step-by-step plan with a coach, but you also get to work alongside them as they help guide you through each step to make sure you are on track to reaching your goals and that you stay in line with your vision.
Contact me today if this article resonated with you and if you want to explore the benefits of coaching when it comes to maintaining your healthy weight, with the support of Christian Counselor at Huntington Beach Christian Counseling.
“Weighing out the Beans”, Courtesy of Tyler Nix, Unsplash.com, CC0 License; “Fruit Breakfast”, Courtesy of Jannis Brandt, Unsplash.com, CC0 License; “Watermelon Smile”, Courtesy of Caju Gomes, Unsplash.com, CC0 License; “Planning”, Courtesy of KOBU Agency, Unsplash.com, CC0 License


 When the day is done and the night closes in, as everyone else sleeps, Addie feels drawn to the kitchen area. The day’s stresses fade away as she begins to relax over the food she finds there. From cookies, chips, and cake to a gallon of chocolate ice cream, she eats all she can manage to get her hands upon. Then she makes her way to her bedroom where more snacks she’s stashed await her.
When the day is done and the night closes in, as everyone else sleeps, Addie feels drawn to the kitchen area. The day’s stresses fade away as she begins to relax over the food she finds there. From cookies, chips, and cake to a gallon of chocolate ice cream, she eats all she can manage to get her hands upon. Then she makes her way to her bedroom where more snacks she’s stashed await her. She is doing all she knows how to do to cope with the way she feels. Therapy has crossed her mind but she thinks she should be able to handle her emotions and feelings on her own. Besides, unleashing all the pain is a scary thought. She doesn’t need the added stress.
She is doing all she knows how to do to cope with the way she feels. Therapy has crossed her mind but she thinks she should be able to handle her emotions and feelings on her own. Besides, unleashing all the pain is a scary thought. She doesn’t need the added stress. Those who have been diagnosed with BED quite often meet additional criteria pertaining to other diagnoses as well. It’s not unusual for them to also display signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and even bipolar disorders. Another typical problem is substance and alcohol abuse. For this reason, a professional who is trained to recognize BED will also generally check for additional diagnoses as well.
Those who have been diagnosed with BED quite often meet additional criteria pertaining to other diagnoses as well. It’s not unusual for them to also display signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and even bipolar disorders. Another typical problem is substance and alcohol abuse. For this reason, a professional who is trained to recognize BED will also generally check for additional diagnoses as well. Eating past the point of feeling full
Eating past the point of feeling full In this age of social media, more and more people, including popular entertainers, are posting their struggles with anxiety.
In this age of social media, more and more people, including popular entertainers, are posting their struggles with anxiety. In CBT, the professional counselor helps the sufferer reframe how they think and how they understand their behavior. In this way, negative thought patterns may hopefully be reduced to something more rational and realistic, preventing these unnecessary mental worries and physical responses to worry.
In CBT, the professional counselor helps the sufferer reframe how they think and how they understand their behavior. In this way, negative thought patterns may hopefully be reduced to something more rational and realistic, preventing these unnecessary mental worries and physical responses to worry. Spiritual self-care, which many today seem to ignore, is very essential as a weak spiritual connection to God makes one very susceptible to all kinds of problems, especially worries about the future. Regular prayer time, reading of Scripture, meaningful Church attendance, and fellowship with other caring believers will do wonders for the spiritual health so that negative, anxious thoughts will not easily bring one down.
Spiritual self-care, which many today seem to ignore, is very essential as a weak spiritual connection to God makes one very susceptible to all kinds of problems, especially worries about the future. Regular prayer time, reading of Scripture, meaningful Church attendance, and fellowship with other caring believers will do wonders for the spiritual health so that negative, anxious thoughts will not easily bring one down. Now while yoga is very helpful for those suffering from anxiety, as a Christian, one must remember to only incorporate the principles of relaxation and mindfulness and not any non-Christian spiritual practices or beliefs. Compromising one’s spiritual beliefs should never be an option.
Now while yoga is very helpful for those suffering from anxiety, as a Christian, one must remember to only incorporate the principles of relaxation and mindfulness and not any non-Christian spiritual practices or beliefs. Compromising one’s spiritual beliefs should never be an option.
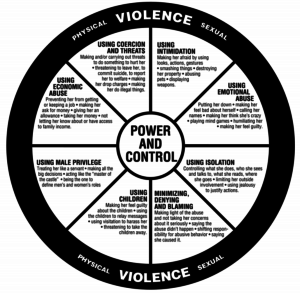
 Domestic abuse does not always happen how you might think. It can start small and build up from there. Often, abusers choose kind-hearted, empathetic victims whose very strengths are used against them. The victims are then manipulated into a life of submission to a controlling, abusive partner.
Domestic abuse does not always happen how you might think. It can start small and build up from there. Often, abusers choose kind-hearted, empathetic victims whose very strengths are used against them. The victims are then manipulated into a life of submission to a controlling, abusive partner. This keeps the victim confused and off-balance. She might think that the latest abusive incident is the last one. She might think it’s her fault, which he would like to convince her of, especially if she responds emotionally or angrily to his treatment of her.
This keeps the victim confused and off-balance. She might think that the latest abusive incident is the last one. She might think it’s her fault, which he would like to convince her of, especially if she responds emotionally or angrily to his treatment of her. Assessing the safety and risks is the important factor. Once a woman begins to make efforts to change the relationship or to leave the situation, the risk of violence increases exponentially. Making a safety plan is paramount if you believe there is even the slightest risk of violence.
Assessing the safety and risks is the important factor. Once a woman begins to make efforts to change the relationship or to leave the situation, the risk of violence increases exponentially. Making a safety plan is paramount if you believe there is even the slightest risk of violence. Anxiety can prevent us from taking part in social activities. It can cause us to have problems at work or keep us from going to gatherings. When we are missing out, it is high time to take a close look at our anxiety and the social phobia it is causing in order to better understand it and to better enable us to get help.
Anxiety can prevent us from taking part in social activities. It can cause us to have problems at work or keep us from going to gatherings. When we are missing out, it is high time to take a close look at our anxiety and the social phobia it is causing in order to better understand it and to better enable us to get help.  Try to get a grip on it through taking deep, controlled breaths. Breathe in through your nose and then out slowly through your mouth, counting to three. Once you have completed the deep breathing exercise, attempt to figure out what the trigger is.
Try to get a grip on it through taking deep, controlled breaths. Breathe in through your nose and then out slowly through your mouth, counting to three. Once you have completed the deep breathing exercise, attempt to figure out what the trigger is. Controlling our focus is the key to stopping the circus. It takes some practice but it can be done. When you think of positive things about yourself, you will find that your anxiousness subsides. A good bit of the worry we have is based on things that are not true. You may feel God is going to punish you for something or that you are going to get a disease. Think of fears you had in the past that never came to pass. That is very helpful in recognizing the unwarranted fears.
Controlling our focus is the key to stopping the circus. It takes some practice but it can be done. When you think of positive things about yourself, you will find that your anxiousness subsides. A good bit of the worry we have is based on things that are not true. You may feel God is going to punish you for something or that you are going to get a disease. Think of fears you had in the past that never came to pass. That is very helpful in recognizing the unwarranted fears. If all environmental factors have been ruled out, it could very well boil down to a psychodynamic contributor, like having an overly critical father or mother who continually made him feel belittled. While this issue is one that can take some time to really work through, there are short-term solutions that can temporarily help to boost his self-confidence.
If all environmental factors have been ruled out, it could very well boil down to a psychodynamic contributor, like having an overly critical father or mother who continually made him feel belittled. While this issue is one that can take some time to really work through, there are short-term solutions that can temporarily help to boost his self-confidence. We’ve all heard of depression, but how much do we really understand about it? It’s often misunderstood in terms of its clinical diagnosis and greatly overused in pop culture.
We’ve all heard of depression, but how much do we really understand about it? It’s often misunderstood in terms of its clinical diagnosis and greatly overused in pop culture.  If you’re noticing that you’re very short-tempered or yelling at your spouse or kids a lot, or otherwise lashing out. Instead of working through your feelings, and identifying their root cause you may project them onto others, blaming those around you for the feelings you have about yourself.
If you’re noticing that you’re very short-tempered or yelling at your spouse or kids a lot, or otherwise lashing out. Instead of working through your feelings, and identifying their root cause you may project them onto others, blaming those around you for the feelings you have about yourself. Another common symptom associated with clinal depression is being extremely restless at night and constantly tired during the day when awake, with little to no motivation to get out of bed to start daily activities. Going to work, or getting the kids on the bus in the morning becomes overwhelming. Even trips to the grocery store may begin to seem like they are simply too much to handle.
Another common symptom associated with clinal depression is being extremely restless at night and constantly tired during the day when awake, with little to no motivation to get out of bed to start daily activities. Going to work, or getting the kids on the bus in the morning becomes overwhelming. Even trips to the grocery store may begin to seem like they are simply too much to handle. It is common for people who are experiencing depression to experience a decreased or complete loss of interest in life. Things that once provided a sense of accomplishment or fulfillment no longer provide any satisfaction. Spending time with friends or family becomes more of a chore as isolation and solitude increase.
It is common for people who are experiencing depression to experience a decreased or complete loss of interest in life. Things that once provided a sense of accomplishment or fulfillment no longer provide any satisfaction. Spending time with friends or family becomes more of a chore as isolation and solitude increase. And even for adolescents, depression is an issue. “In 2015, an estimated 3 million adolescents age 12 to 17 in the United States had at least one major depressive episode in the previous year, according to the National Institute of Mental Health.” (ADAA.org)
And even for adolescents, depression is an issue. “In 2015, an estimated 3 million adolescents age 12 to 17 in the United States had at least one major depressive episode in the previous year, according to the National Institute of Mental Health.” (ADAA.org) In recent years, yoga has become quite popular in Western culture as a way to keep the body and mind strong.
In recent years, yoga has become quite popular in Western culture as a way to keep the body and mind strong. When depressed, a sufferer may feel that their spirit is at an all-time low, making it easier to succumb to negative thoughts about self-harm (e.g. suicide, alcohol or drug abuse) or breaking relationships (e.g. divorce, running away, isolation). This is why it is very important for the sufferer to reconnect with God.
When depressed, a sufferer may feel that their spirit is at an all-time low, making it easier to succumb to negative thoughts about self-harm (e.g. suicide, alcohol or drug abuse) or breaking relationships (e.g. divorce, running away, isolation). This is why it is very important for the sufferer to reconnect with God.